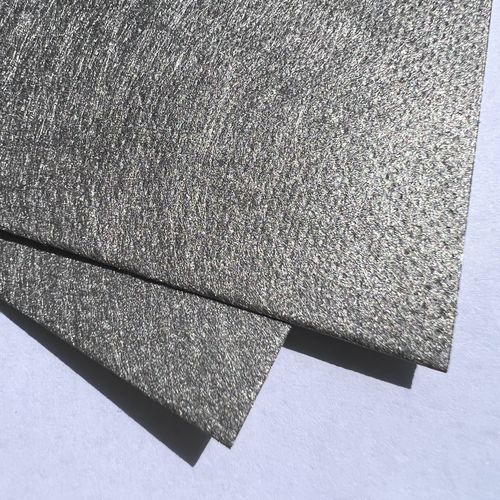
Stainless steel sintered felt is a filtration medium made from stainless steel fibers through high-temperature sintering. It has characteristics such as high porosity, excellent air permeability, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance. Below is the typical manufacturing process for stainless steel sintered felt:
1. Fiber Preparation
- Raw Material Selection: High-quality stainless steel materials, such as 304 or 316L, are used to create fine metal fibers through melting and drawing processes.
- Fiber Cutting: Stainless steel materials are processed into fine filaments of specific lengths and diameters, typically ranging from a few microns to tens of microns.
2. Fiber Layering
- Non-woven Fabric Formation: Stainless steel fibers are randomly laid to form a non-woven fabric. This process is done through airflow or mechanical means, ensuring uniform fiber distribution to create the desired porosity and thickness.
- Layering Structure: Different layers of fibers with varying thicknesses and porosities are stacked according to the design requirements to ensure both filtration performance and mechanical strength.
3. Cold Pressing
- Pressing Process: The stacked stainless steel fiber non-woven fabric is placed in a mold, where it undergoes a pre-pressing process. This step helps initially fix the fiber layers' shape and enhances their structural stability.
4. Vacuum Sintering
- High-Temperature Sintering: The pre-pressed fiber felt is placed in a vacuum sintering furnace for high-temperature sintering, typically at temperatures between 900°C and 1200°C.
- Sintering Process: Under high temperatures, the contact points between the metal fibers undergo diffusion bonding, forming a solid mesh structure, which gives the felt high strength and durability.
5. Cooling and Annealing
- Cooling Process: After sintering, the material needs to cool down slowly to ensure structural stability and prevent deformation caused by rapid cooling.
- Annealing: Annealing is often performed to relieve stress created during sintering, improving the toughness and service life of the product.
6. Cutting and Processing
- Size Cutting: The sintered stainless steel felt is cut to specific sizes or shapes based on customer requirements or design specifications. Laser cutting or waterjet cutting methods are commonly used.
- Shaping: Depending on the application, the sintered felt can be processed into various shapes such as circular, rectangular, or other complex forms, suitable for different equipment and filter needs.
7. Surface Treatment
- Polishing or Pickling: Depending on the application, surface treatments like polishing or pickling may be applied to improve the felt's corrosion resistance or ensure its surface smoothness for certain environments.
8. Performance Testing
- Porosity and Thickness Testing: The porosity and thickness of the sintered felt are tested to ensure compliance with design specifications.
- Strength and Permeability Testing: Mechanical strength and air permeability tests are conducted to ensure stable performance during filtration.
- Filtration Accuracy Testing: Filtration experiments are performed to verify the actual filtration precision of the sintered felt, ensuring it meets the filtration requirements for specific applications.
9. Final Packaging
- Cleaning and Drying: The final product is cleaned to remove any impurities from the production process and dried to ensure cleanliness.
- Packaging and Shipment: Proper packaging is carried out to protect the product from damage during transportation.
These processes produce stainless steel sintered felt with excellent high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, strength, and stable filtration accuracy. It is widely used in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, petroleum, and gas filtration systems.